Concepts#
This library is a collection of DataFusion extensions that enable distributed query execution. You can think of it as normal DataFusion, with the addition that some nodes are capable of streaming data over the network using Arrow Flight instead of through in-memory communication.
Key terminology:
Stage: a portion of the plan separated by a network boundary from other parts of the plan. A plan contains one or more stages, each separated by network boundaries.Task: a unit of work in a stage that executes the inner plan in parallel to other tasks within the stage. Each task in a stage executes a structurally identical plan in different worker, passing atask_indexas a contextual value for making choices about what data should be returned.Network Boundary: a node in the plan that streams data from a network interface rather than directly from its children nodes.Worker: a physical machine listening to serialized execution plans over an Arrow Flight interface. A task is executed by exactly one worker, but one worker executes many tasks concurrently.
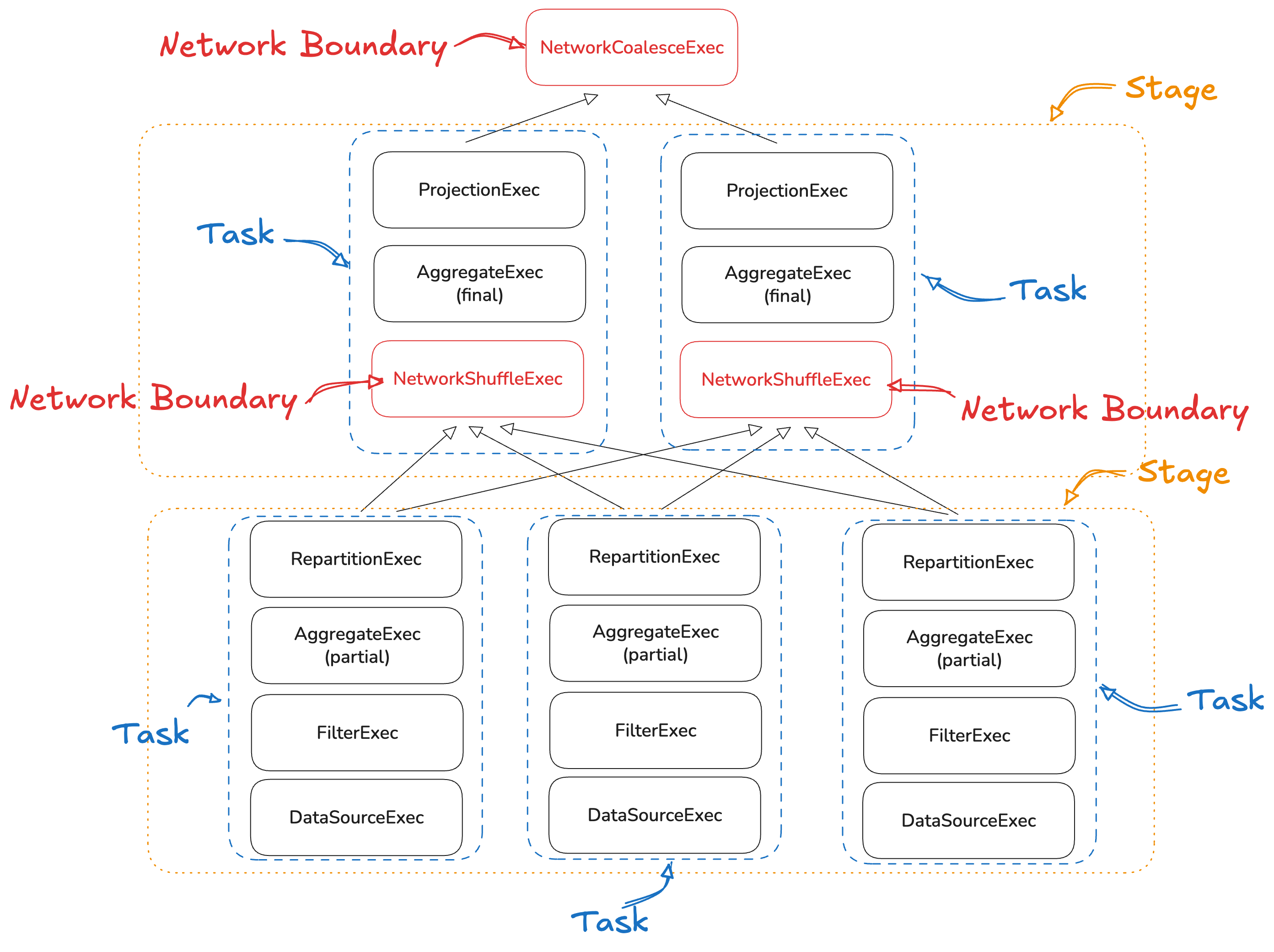
You’ll see these concepts mentioned extensively across the documentation and the code itself.
Public API#
Some other more tangible concepts are the structs and traits exposed publicly, the most important are:
DistributedPhysicalOptimizerRule#
A physical optimizer rule that transforms single-node DataFusion query plans into distributed query plans. It reads a fully formed physical plan and injects the appropriate nodes to execute the query in a distributed fashion.
It builds the distributed plan from bottom to top, injecting network boundaries at appropriate locations based on the nodes present in the original plan.
Worker#
Arrow Flight server implementation that integrates with the Tonic ecosystem and listens to serialized plans that get executed over the wire.
Users are expected to build these and spawn them in ports so that the network boundary nodes can reach them.
WorkerResolver#
Determines the available workers in the Distributed DataFusion cluster by returning their URLs.
Different organizations have different networking requirements—from Kubernetes deployments to cloud provider solutions. This trait allows Distributed DataFusion to adapt to various scenarios.
TaskEstimator#
Estimates the number of tasks required in the leaf stage of a distributed query.
The number of tasks each stage has is determined from bottom to top. This means that leaf stages will decide how many tasks they need to execute based on the amount of data their leaf nodes will pull. Upper stages will have their number of tasks reduced or increased depending on how much the cardinality of the data was reduced in previous stages.
DistributedTaskContext#
An extension present during the ExecutionPlan::execute() that contains information about the current task in
which the plan is being executed.
As a user, you will need to interact with this type in your custom leaf nodes, as depending on which task index you are in, you might want to return a different set of data.
For example, if you are on the task with index 0 of a 3-task stage, you might want to return only the first 1/3 of the data. If you are on the task with index 2, you might want to return the last 1/3 of the data, and so on.
ChannelResolver#
Optional extension trait that allows to customize how connections are established to workers. Given one of the
URLs returned by the WorkerResolver, it builds an Arrow Flight client ready for serving queries.